Over the past two decades, organizations like the Institute for Healthcare Improvement have identified that too many patients are dying from preventable causes.
The 2019 ECRI Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns illustrate this clearly1:
#6 Detecting Changes in a Patient's Condition
Failure to detect changes in a patient’s condition is an ongoing patient safety concern across the continuum of care. Problems can arise within a care unit and during transitions of care within a facility and from one facility to another.1
#8 Early Recognition of Sepsis across the Continuum
Sepsis can be difficult to detect, but early recognition is vital because sepsis can quickly turn deadly. “We’re in a time rush,” says James Davis, MSN, RN, CCRN-K, HEM, CIC, FAPIC, senior infection prevention and patient safety analyst/consultant, ECRI Institute. The challenge is, “Can we intervene quicker to get patients the care they need to prevent shock and death?”1
Signs can appear earlier than you may think:
6-8 Hours
Before a critical event occurs, warning signs can often be identified2


Patient Deterioration has real financial implications. Use our Patient Deterioration Burden Calculator to explore the Financial Burden of Patient Deterioration for your hospital.
The challenge of early recognition of patient deterioration has been a persistent issue and a lingering patient safety concern.

In the case of Sepsis, every hour counts:

Heart Rate & Respiratory rate are leading indicators of patient deterioration5
To help detect deterioration early, accurate capture of vital signs including heart rate & respiratory rate is critical. But we all know that Q4 and even Q2 vitals can be difficult to manage.
Respiratory rate – the single leading indicator of patient deterioration – is the least often recorded and most omitted vital signs. 6,7
Switch From Subjective to Objective
In one study, nurses recorded nearly 72% of all respiratory rates as either 18 or 20 bpm, whereas only 13% measured by trained observers had these values.8
This confirms a significant bias and/or multiplication artifact with visual assessment. 8

You may be thinking
We use early warning scores, so we know when patients are deteriorating. Well – early warning scores are only as good as their inputs – inaccurate vital sign inputs like RR can make EWS less valuable.
And monitoring solutions like telemetry may not accurately capture respiratory rate – the single leading indicator of deterioration.
What if we told you
All your med-surg patients could have their heart rate and respiratory rate continuously monitored just by laying in bed?

The Centrella Smart+ bed is the only Med-Surg bed that comes standard with Contact-Free, Continuous Monitoring.
Contact-Free, Continuous Monitoring can help save lives9:

86% reduction in code blue events following implementation of Contact-Free, Continuous Monitoring in a chart review study9

45% reduction in number of ICU days on patients transferred from med-surg9

9% reduction in length of stay9
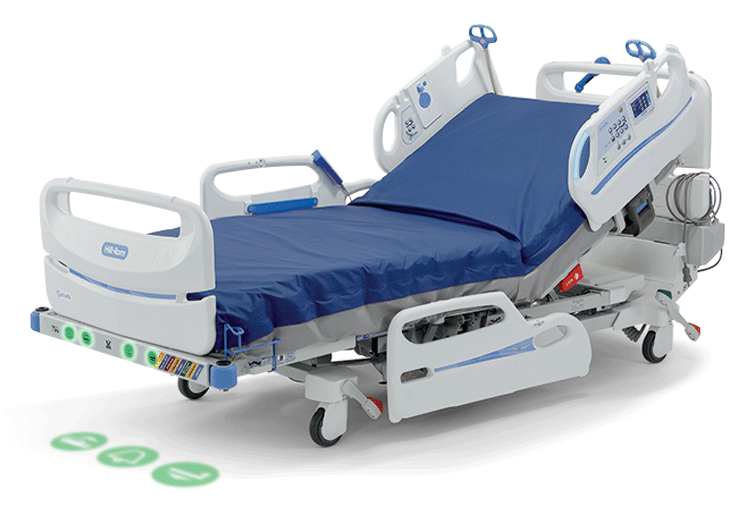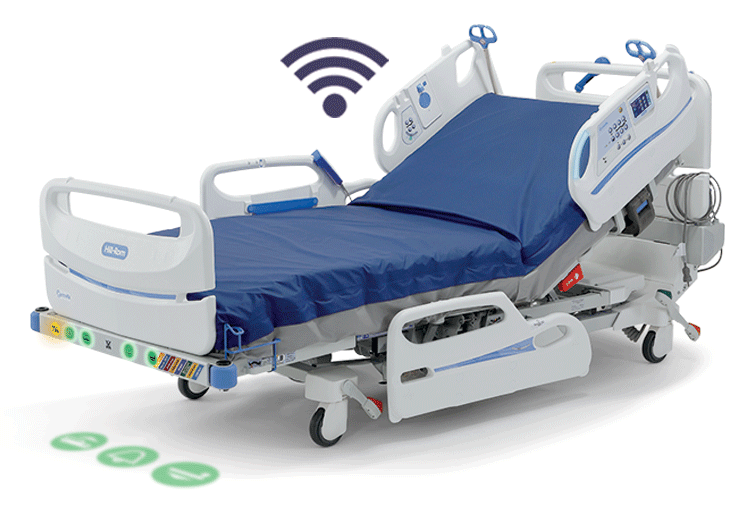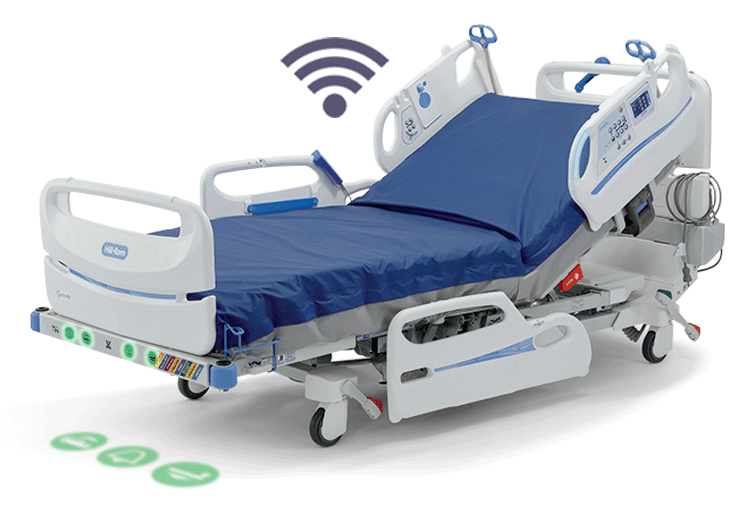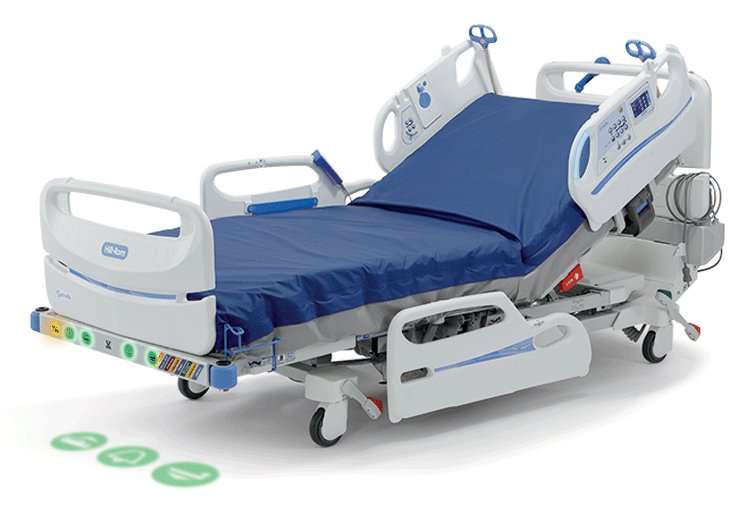
SEE HOW IT WORKS:

STEP 1
Monitoring
A sensor that is installed under the mattress detects cardiac and respiratory motion.

STEP 2
Detection
The sensor updates the HR/RR values twice per second. This information is compiled in an algorithm that creates a running trend of HR/RR.
STEP 3
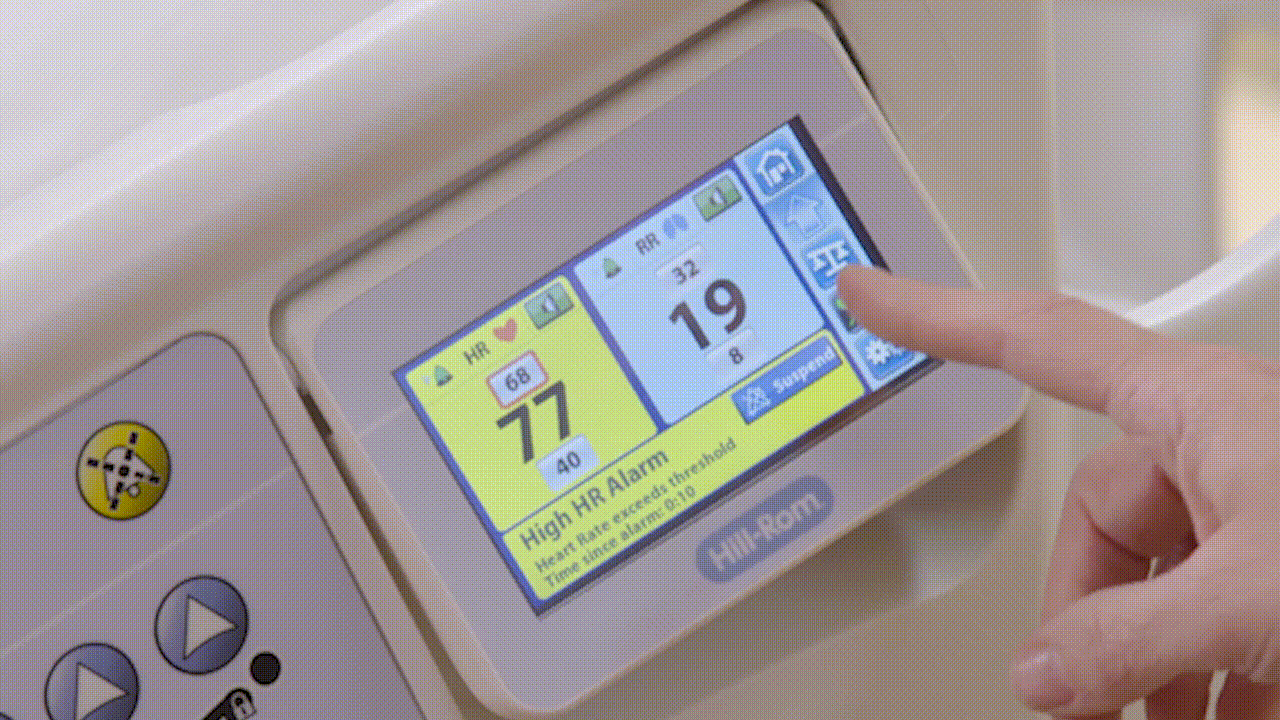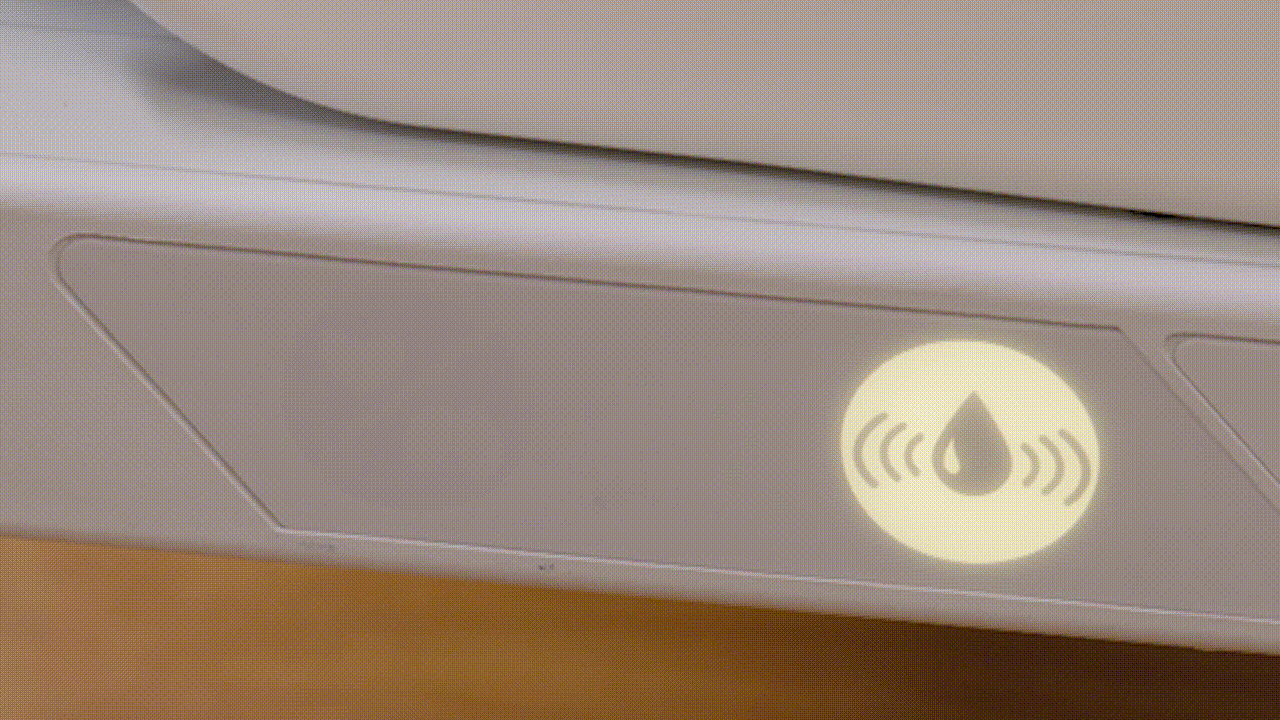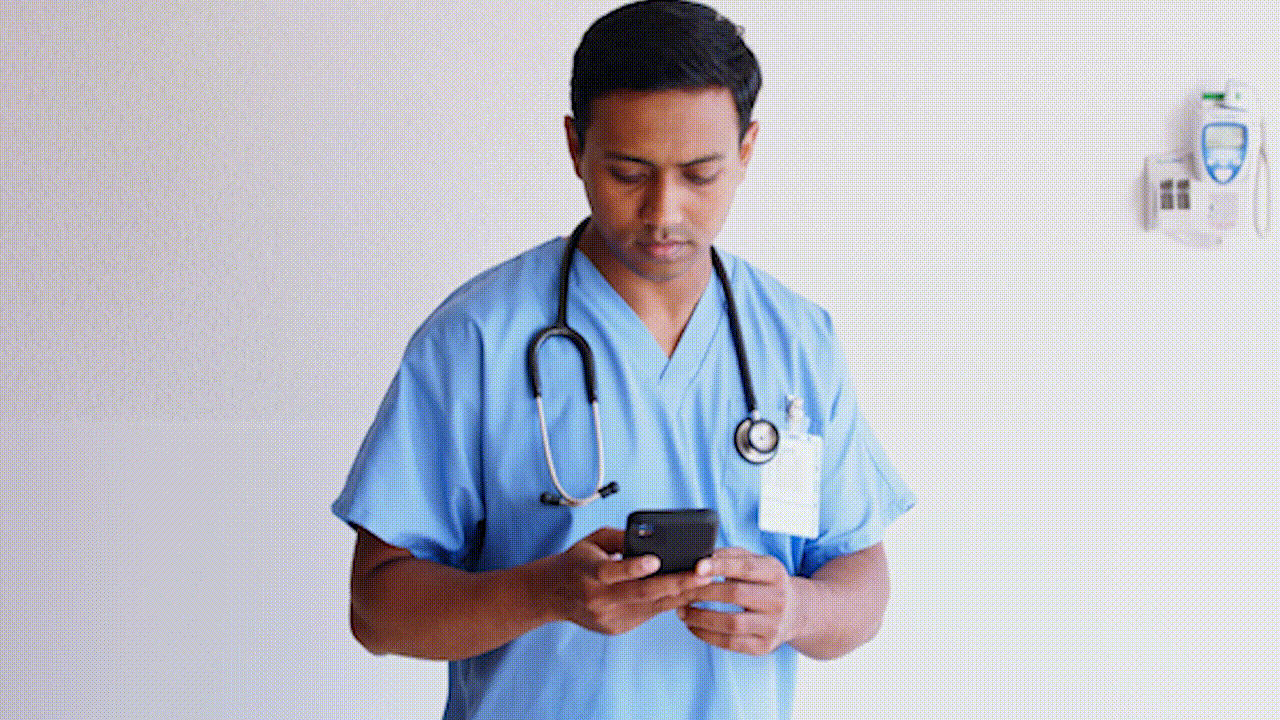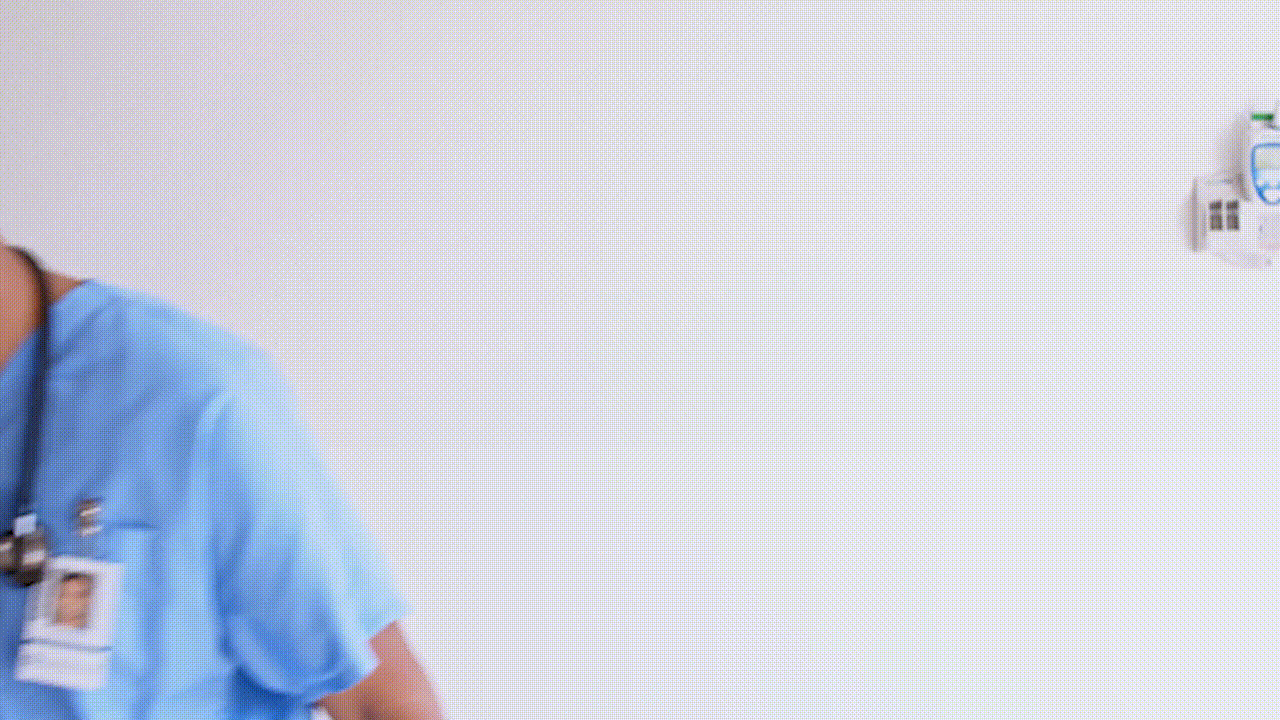
Alerting
When HR/RR exceeds one of the set thresholds, the bed will alert via local alerts and through customizable alerts via the nurse call system.
Patient Safety is something we must all focus on
And Hillrom believes, like those other organizations, that no patient should die from preventable causes. We want every Med-Surg patient to be monitored for the earliest indicators of deterioration – and now, we can do that. And so can you.
Keep a Watchful Eye
Keep your patients on the path to recovery with the right intelligence. Along with pressure injury prevention, smart solutions for continuous patient monitoring can help you ensure you have the best solutions to help keep your patients safe.
References
- ECRI Institute. 2019 Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns.
- Zimlichman, et al. Contactless respiratory and heart rate monitoring: validation of an innovative tool. J of Med Eng & Tech, Vol. 34, Nos 7-8,Oct-Nov 2010, 393-398.
- Sepsis Alliance. Sepsis.org. Sepsis Fact Sheet.
- Page D MD, et al. Community-, Healthcare- and Hospital-Acquired Severe Sepsis Hospitalizations in the University HealthSystem Consortium. Crit Care Med. 2015 Sept: 43(9): 1945-1951.
- MC11587: Welch Allyn White Paper: Telemetry Monitoring on the Medical/Surgical Floor.
- Churpek MM, Adhikari R, Edelson DP. The value of vital sign trends for detecting clinical deterioration on the wards. Resuscitation. 2016;102:1-5.
- Elliot, M. (2016). Why is Respiratory Rate the Neglected Vital Sign? A Narrative Review. Inter Arch of Nursing and Healthcare.
- Semler, MW et al, Flash mob research: a single-day, multicenter, resident-directed study of respiratory rate. Chest. 2013;143:1740–1744.
- Brown Harvey, et al. The American Journal of Medicine. 2014; 127:226-232.